What is Alopecia?
Alopecia is a medical term used to describe hair loss. It is usually seen as thinning of the scalp hair but can also affect other parts of the body, such as the beard, eyebrows, and eyelashes. Alopecia can be divided into two types: scarring and non-scarring alopecia. Scarring alopecia is permanent while non-scarring alopecia may be reversible.
Symptoms
• Patchy or circular bald spots on the scalp, face, and other parts of the body
• Thinning of the hair on the scalp
• Complete baldness (alopecia totalis)
• Excessive shedding of hair
• Changes in hair texture
• Scalp inflammation or itching
• Loss of eyebrows, eyelashes, or other body hair
Causes of Alopecia
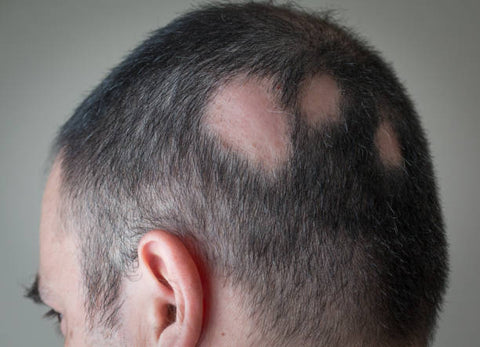
• Genetics: Alopecia can be inherited from a parent.
• Autoimmune Disorders: Alopecia is an autoimmune disorder, where the body’s immune cells attack the hair follicles.
• Hormonal Imbalance: Hormonal imbalances such as those caused by thyroid disease can lead to alopecia.
• Stress: Stress can cause the body to release hormones that can lead to alopecia.
Types of Alopecia
• Alopecia Areata: This is the most common form of alopecia and involves patchy hair loss. The patches can range in size from a few millimeters to several centimeters.
• Alopecia Totalis: This is an advanced form of alopecia areata, where all the hair on the scalp is lost.
• Alopecia Universalis: This is the most severe form of alopecia, where all hair on the body is lost.
• Scarring Alopecia: This is a type of alopecia that results in permanent hair loss due to scarring of the scalp.
Living With Alopecia
• Coping Strategies: It is important to find ways to cope with the physical and emotional effects of alopecia. This can include talking to a therapist or joining a support group.
• Wigs and Hairpieces: Wigs and hairpieces can help to restore a sense of normalcy for those with alopecia.
• Makeup and Tattoos: Makeup and tattoos can help to conceal the effects of alopecia.
Treatment Options for Alopecia
There are several treatment options for alopecia, including medications, laser therapy, and surgery. The type of treatment chosen will depend on the type of alopecia, its severity, and the overall health of the patient.
Medications
Medications such as minoxidil and finasteride are commonly used to treat alopecia. Minoxidil is a topical solution that is applied directly to the scalp, while finasteride is taken orally. Both medications can help to slow or stop the progression of alopecia but may not be effective in all cases.
Laser Therapy
Laser therapy is a relatively new treatment for alopecia. It uses low-level laser light to stimulate the scalp and encourage hair growth. Laser therapy is usually done on an outpatient basis and may take several weeks to show results.
Surgery
In some cases, surgery may be recommended to treat alopecia. Surgery may involve the removal of scar tissue from the scalp, or the transplantation of hair follicles from another part of the body. Surgery is usually done as an outpatient procedure and may require several months for the results to be seen.
Conclusion
Alopecia is a medical condition that affects many people. It is important to seek the advice of a qualified healthcare professional to determine the best treatment plan for your specific situation. With proper diagnosis and treatment, alopecia can be successfully managed and its effects minimized.












