Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), also known as polycystic ovary disorder (PCOD), is a hormonal disorder that affects women of reproductive age. PCOD is a common condition that can have a significant impact on a woman's fertility, menstrual cycle, and overall health.
What is PCOD?
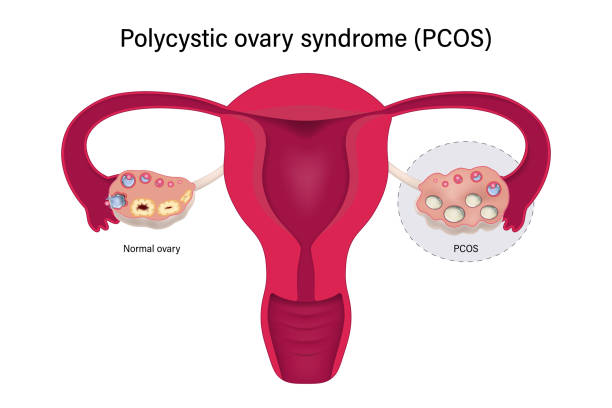
PCOD is a condition that occurs when a woman's body produces too many male hormones (androgens). These hormones can interfere with the normal functioning of the ovaries, causing them to produce small cysts (fluid-filled sacs) that may affect ovulation. Women with PCOD may have irregular periods, difficulty getting pregnant, and other health problems.
Causes of PCOD
The exact cause of PCOD is not known, but researchers believe that several factors may contribute to its development, including:
-
Insulin resistance: Women with PCOD are often resistant to insulin, which can cause the body to produce more insulin to compensate. This increased insulin production can lead to an overproduction of androgens and the development of cysts on the ovaries.
-
Genetics: There may be a genetic component to PCOD, as it tends to run in families.
-
Inflammation: Chronic inflammation can also contribute to the development of PCOD.
Symptoms of PCOD
The symptoms of PCOD can vary from woman to woman and can include:
-
Irregular periods or no periods at all
-
Heavy periods
-
Acne
-
Excessive hair growth on the face, chest, or back
-
Weight gain or difficulty losing weight
-
Fatigue
-
Mood changes
-
Headaches
-
Infertility
Diagnosis of PCOD
To diagnose PCOD, your healthcare provider may perform a physical exam, pelvic exam, and blood tests to check hormone levels. They may also order an ultrasound to check for cysts on the ovaries.
Treatment of PCOD
There is no cure for PCOD, but treatment can help to manage symptoms and reduce the risk of complications. Treatment options may include:
-
Lifestyle changes: Eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight can help to reduce symptoms and improve overall health.
-
Medications: Birth control pills, metformin (a medication used to treat diabetes), and anti-androgen medications may be prescribed to help regulate menstrual cycles and reduce symptoms.
-
Fertility treatments: Women who are having difficulty getting pregnant may be prescribed medications to help stimulate ovulation or may undergo assisted reproductive technologies like in vitro fertilization (IVF).
-
Surgery: In rare cases, surgery may be recommended to remove cysts on the ovaries or to reduce androgen production.
FAQs about PCOD
What causes PCOD?
The exact cause of PCOD is not known, but genetics, insulin resistance, and hormonal imbalances are believed to be contributing factors.
How is PCOD diagnosed?
PCOD is usually diagnosed through a combination of physical exams, medical history, blood tests, and ultrasound scans.
Can PCOD be cured?
PCOD cannot be cured, but it can be managed with a healthy diet, regular exercise, and medications such as birth control pills or insulin-sensitizing drugs.
How does PCOD affect fertility?
PCOD can affect fertility by preventing ovulation, which can make it more difficult to conceive. However, with proper treatment, many women with PCOD are able to get pregnant.
How can I manage PCOD symptoms?
Managing PCOD symptoms involves maintaining a healthy weight through regular exercise and a healthy diet, managing stress levels, and taking medication as prescribed by a healthcare provider.
Is PCOD linked to other health problems?
PCOD is linked to other health problems such as diabetes, high blood pressure, heart disease, and endometrial cancer. Therefore, it is important for women with PCOD to monitor their health closely and seek medical care when necessary.
Can PCOD affect a woman's mental health?
PCOD can affect a woman's mental health by causing anxiety, depression, and other mood disorders. Therefore, it is important to seek emotional support and treatment for these issues as well.
How common is PCOD?
PCOD is a common condition that affects up to 10% of women of reproductive age.
Are pcos and pcod same?
PCOD (Polycystic Ovary Disease) and PCOS (Polycystic Ovary Syndrome) are two terms that are often used interchangeably, but they do have some differences. PCOD is a condition in which multiple cysts develop on the ovaries, and the ovaries may be enlarged. PCOS, on the other hand, is a hormonal disorder that involves a range of symptoms including ovarian cysts, irregular periods, excess hair growth, and acne.
PCOS is considered to be a more comprehensive term that encompasses both the ovarian cysts and hormonal imbalances, whereas PCOD is mainly focused on the cysts themselves. In practical terms, the two terms are often used interchangeably, and both conditions can have similar symptoms and treatment options.
Can a pcod patient get pregnant
Yes, a woman with PCOD (Polycystic Ovary Disease) can get pregnant, although it may be more challenging. One of the main issues with PCOD and fertility is that women with this condition often have irregular or absent periods, which can make it difficult to know when ovulation is occurring. Ovulation is necessary for conception to occur, so women with PCOD may need help from a healthcare provider to track ovulation and optimize the chances of conception.
There are several treatment options available to help women with PCOD get pregnant, such as ovulation induction medications (such as Clomid or Letrozole), intrauterine insemination (IUI), or in vitro fertilization (IVF). It is important for women with PCOD who want to become pregnant to work closely with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses their specific needs and goals.
It is also important for women with PCOD to manage their overall health, as lifestyle factors such as weight, diet, and exercise can affect fertility. Maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet, and getting regular exercise can all help improve fertility outcomes in women with PCOD.
Can pcod be cured naturally
PCOD (Polycystic Ovary Disease) cannot be cured naturally, as it is a chronic condition that requires ongoing management. However, making certain lifestyle changes can help alleviate symptoms and improve overall health in women with PCOD. Here are some natural ways to manage PCOD:
-
Maintain a healthy weight: Women with PCOD are more likely to be overweight or obese, which can worsen symptoms and increase the risk of other health problems. Losing weight and maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise can help regulate insulin levels and improve hormone balance.
-
Eat a healthy diet: Eating a diet rich in whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean protein, and healthy fats can help reduce inflammation in the body and regulate insulin levels. Avoiding processed foods, sugary drinks, and high-fat foods can also help improve overall health in women with PCOD.
-
Exercise regularly: Regular exercise can help improve insulin sensitivity, reduce inflammation, and promote weight loss. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week.
-
Manage stress: High levels of stress can exacerbate PCOD symptoms and disrupt hormone balance. Practicing stress-management techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises can help reduce stress levels and improve overall health.
-
Get enough sleep: Lack of sleep can worsen PCOD symptoms and increase insulin resistance. Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep each night to promote hormone balance and overall health.
While these lifestyle changes can be helpful for managing PCOD, it is important to work closely with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses individual needs and goals. In some cases, medication or other medical interventions may be necessary to manage PCOD symptoms.
Do PCOD affects pregnancy
PCOD (Polycystic Ovary Disease) can affect pregnancy in a number of ways, although many women with PCOD are able to have successful pregnancies. Some of the ways that PCOD can affect pregnancy include:
- Women with PCOD may have difficulty getting pregnant due to irregular ovulation or absent periods. However, there are several treatment options available, such as ovulation induction medications (such as Clomid or Letrozole), intrauterine insemination (IUI), or in vitro fertilization (IVF), that can help women with PCOD conceive.
- Women with PCOD may have an increased risk of miscarriage, especially if their PCOD is not well-managed. However, with proper medical care and management of PCOD symptoms, many women with PCOD are able to have successful pregnancies without experiencing a miscarriage.
- Women with PCOD are at an increased risk of developing gestational diabetes during pregnancy, which can affect the health of the mother and the baby. It is important for women with PCOD to work closely with their healthcare provider to monitor blood sugar levels and manage gestational diabetes if it occurs.
- Women with PCOD may have an increased risk of developing pre-eclampsia, a serious pregnancy complication that can affect the mother's health and the baby's growth and development. Regular prenatal care and monitoring can help detect and manage pre-eclampsia if it occurs.
It is important for women with PCOD who are pregnant or planning to become pregnant to work closely with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses their specific needs and goals. With proper care and management, most women with PCOD are able to have successful pregnancies and healthy babies.
Is pcod is a serious problem
PCOD (Polycystic Ovary Disease) is a common hormonal disorder that affects many women of reproductive age. While PCOD is not typically considered a life-threatening condition, it can cause a range of symptoms that can affect a woman's quality of life and overall health.
Some of the potential complications of PCOD include:
-
Infertility: PCOD is one of the leading causes of infertility in women. Women with PCOD may have difficulty getting pregnant due to irregular ovulation or absent periods.
-
Metabolic issues: Women with PCOD are at increased risk of developing metabolic issues such as insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol.
-
Endometrial cancer: Women with PCOD may be at increased risk of developing endometrial cancer due to irregular periods and a buildup of uterine lining.
-
Sleep apnea: Women with PCOD are at increased risk of developing sleep apnea, a serious sleep disorder that can affect overall health.
-
Depression and anxiety: Women with PCOD may be at increased risk of depression and anxiety due to the impact of PCOD on quality of life.
While PCOD can be a serious problem, it is important to note that with proper care and management, most women with PCOD are able to lead healthy and fulfilling lives. It is important for women with PCOD to work closely with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses their specific needs and goals.
PCOD diet chart for weight loss
- Breakfast:
- 1 cup cooked oats with ½ cup mixed berries and 1 tablespoon chia seeds
- 1 boiled egg
- 1 cup green tea
- Mid-morning snack:
- 1 small apple
- 10 almonds
- Lunch:
- 1 cup mixed salad with 1 tablespoon olive oil dressing
- 1 small bowl of brown rice
- 1 cup vegetable curry or lentil soup
- Afternoon snack:
- 1 small bowl of mixed fruits
- 1 small cup of unsweetened yogurt
- Dinner:
- Grilled chicken breast or baked fish
- 1 cup mixed veggies (broccoli, carrots, cauliflower, zucchini, etc.)
- 1 small bowl of quinoa
- Bedtime snack:
- 1 glass of low-fat milk
Tips for following a PCOD diet chart for weight loss:
- Eat a small meal or snack every 3-4 hours to keep your metabolism active
- Avoid processed foods, sugary drinks, and high-fat foods
- Choose whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean protein, and healthy fats
- Drink plenty of water throughout the day to stay hydrated
- Limit caffeine and alcohol consumption
It is important to work closely with a registered dietitian or healthcare provider to develop a personalized diet plan that meets your specific needs and goals.
Conclusion
PCOD is a common condition that can have a significant impact on a woman's health and fertility. If you are experiencing symptoms of PCOD, it's important to speak with your healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. By managing symptoms and taking steps to improve overall health, women with PCOD can live healthy, fulfilling lives.












