Mouth cancer, also known as oral cancer, is a type of cancer that can occur in any part of the mouth, including the lips, tongue, gums, and cheeks. In this blog post, we will discuss the causes, symptoms, treatment, and prevention of mouth cancer.
Causes of Mouth Cancer
The primary cause of mouth cancer is the use of tobacco products, including cigarettes, cigars, and chewing tobacco. Other risk factors include:
-
Heavy alcohol consumption
-
Exposure to the human papillomavirus (HPV)
-
Prolonged sun exposure to the lips
-
Poor oral hygiene
-
Family history of mouth cancer
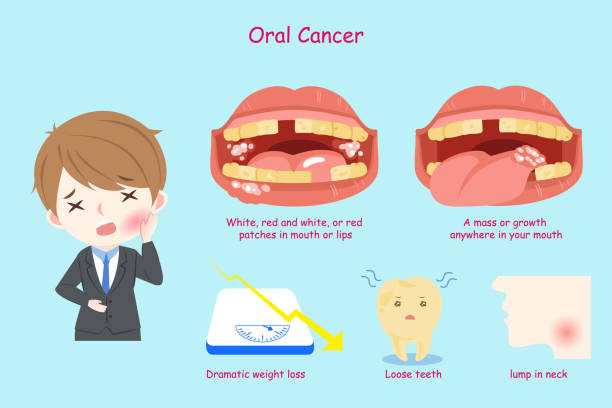
Symptoms of Mouth Cancer
The symptoms of mouth cancer can vary depending on the location and stage of the cancer. In the early stages, there may be no symptoms at all. As the cancer progresses, symptoms may include:
-
Persistent sore throat or hoarseness
-
A lump or thickening in the mouth or throat
-
Red or white patches in the mouth
-
Numbness or tingling in the mouth or lips
-
Difficulty chewing, swallowing, or speaking
-
Unexplained bleeding or pain in the mouth
Stages in Mouth Cancer
-
Stage 0: This is the earliest stage of mouth cancer, where abnormal cells are present but have not spread beyond the surface layer of the mouth. At this stage, the cancer is still considered to be precancerous and can often be treated with surgery or radiation therapy.
-
Stage I: At this stage, the cancer is still small and has not spread to nearby lymph nodes. Treatment options may include surgery or radiation therapy.
-
Stage II: At this stage, the cancer is larger and may have spread to nearby lymph nodes. Treatment options may include surgery, radiation therapy, or a combination of both.
-
Stage III: At this stage, the cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes and may be affecting other tissues or organs in the area. Treatment options may include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or a combination of these treatments.
-
Stage IV: This is the most advanced stage of mouth cancer, where the cancer has spread to distant organs, such as the lungs, liver, or bones. Treatment options may include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, targeted therapy, or a combination of these treatments.
Treatment of Mouth Cancer
Treatment of mouth cancer depends on several factors, including the size and location of the tumor, how advanced the cancer is, and your overall health. Here are the most common treatments for mouth cancer:
-
Surgery: Surgery is the most common treatment for mouth cancer. Depending on the location and size of the tumor, your doctor may remove all or part of the affected area. This can involve removing part of the tongue, jawbone, or other surrounding tissues. In some cases, reconstructive surgery may be necessary.
-
Radiation therapy: Radiation therapy uses high-energy beams to kill cancer cells. It can be used as the primary treatment or in combination with surgery or chemotherapy. Depending on the location of the tumor, your doctor may use external radiation, which is directed from outside the body, or brachytherapy, which involves placing a radioactive material directly into the tumor.
-
Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells. It can be used alone or in combination with surgery or radiation therapy. Chemotherapy is often used to treat advanced stages of mouth cancer, or when the cancer has spread to other parts of the body.
-
Immunotherapy: Immunotherapy is a type of treatment that uses your own immune system to fight cancer cells. It can be used in combination with other treatments, and it works by stimulating your immune system to attack the cancer cells.
-
Targeted therapy: Targeted therapy uses drugs that specifically target the cancer cells. These drugs work by blocking specific proteins that help cancer cells grow and divide.
-
Palliative care: Palliative care focuses on improving the quality of life for people with advanced cancer. This can include managing symptoms like pain and difficulty swallowing, as well as providing emotional support and counseling.
It's important to note that the treatment of mouth cancer can be complex and may involve a combination of these approaches. Your doctor will work with you to develop a treatment plan that is tailored to your specific needs and circumstances. Early detection and treatment are key to improving the chances of successful treatment and recovery.
Prevention of Mouth Cancer
The best way to prevent mouth cancer is to avoid or limit the use of tobacco products and alcohol. Other ways to reduce your risk of mouth cancer include:
-
Practicing good oral hygiene
-
Using lip balm with sun protection
-
Seeking treatment for persistent mouth sores or lumps
-
Eating a healthy diet rich in fruits and vegetables
-
Exercising regularly
In conclusion, mouth cancer is a serious and potentially deadly disease. However, by understanding the causes, symptoms, treatment, and prevention of mouth cancer, you can take steps to protect yourself and seek medical attention if necessary. Remember to avoid or limit the use of tobacco and alcohol, maintain good oral hygiene, and seek medical care if you experience any symptoms of mouth cancer. Early detection and treatment can greatly improve the chances of successful treatment and recovery.












