Malaria is a potentially life-threatening disease caused by a parasite that is transmitted to humans through the bite of infected mosquitoes. It is a major public health concern in many parts of the world, especially in sub-Saharan Africa, where it is a leading cause of death. In this blog post, we will explore the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for malaria.
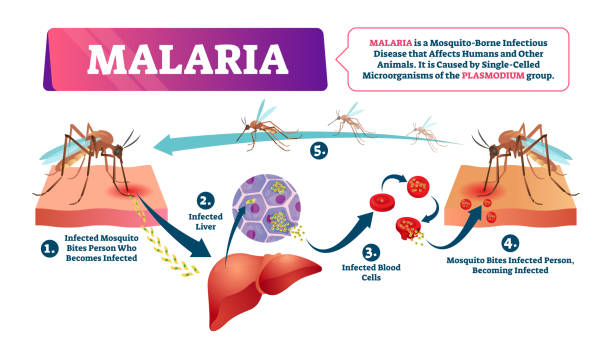
Causes of Malaria
Malaria is caused by Plasmodium parasites that are transmitted to humans through the bites of infected female Anopheles mosquitoes. The parasites enter the bloodstream and infect the liver and red blood cells, where they multiply and cause symptoms.
Symptoms of Malaria

The symptoms of malaria can vary depending on the severity of the infection, but commonly include:
-
High fever
-
Chills
-
Headache
-
Muscle aches
-
Fatigue
-
Nausea and vomiting
-
Diarrhea
-
Jaundice
-
Convulsions
Diagnosis of Malaria
If you are experiencing any symptoms of malaria, it is important to see a healthcare professional for an evaluation. Diagnosis is typically made by a blood test that looks for the presence of Plasmodium parasites in the bloodstream.
Treatments of Malaria
Malaria can be treated with a variety of antimalarial medications, which work by killing the Plasmodium parasites in the body. The choice of medication and duration of treatment will depend on the type of malaria, the severity of the infection, and the individual's health status.
Prevention of Malaria
There are several ways to prevent malaria, including:
-
Use mosquito nets: Sleeping under an insecticide-treated mosquito net can help prevent mosquito bites and reduce the risk of malaria.
-
Use insect repellent: Applying insect repellent containing DEET or picaridin can help prevent mosquito bites.
-
Take antimalarial medication: If you are traveling to an area where malaria is prevalent, it is important to take antimalarial medication as prescribed by a healthcare professional.
-
Wear protective clothing: Wearing long-sleeved shirts and pants can help reduce the amount of exposed skin that mosquitoes can bite.
-
Eliminate standing water: Mosquitoes breed in standing water, so eliminating sources of stagnant water around your home can help reduce the mosquito population.
In conclusion, malaria is a serious and potentially life-threatening disease that requires prompt diagnosis and treatment. By taking appropriate measures to prevent mosquito bites and seeking medical attention if you experience symptoms of malaria, you can help protect yourself from this disease. Remember to consult with a healthcare professional for individualized advice on preventing and treating malaria.












