Lung cancer is a type of cancer that starts in the lungs and can spread to other parts of the body. It is the leading cause of cancer deaths worldwide. In this blog post, we will discuss the causes, symptoms, treatment, and prevention of lung cancer.
Stages in Lung Cancer
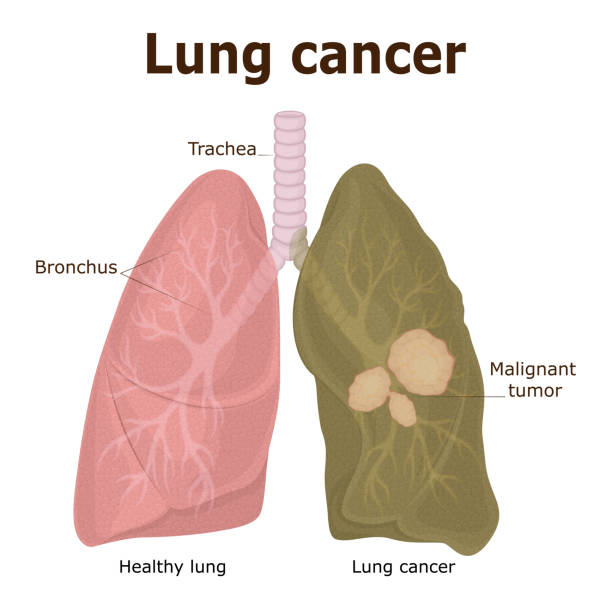
Lung cancer is typically categorized into two main types: non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and small cell lung cancer (SCLC). Each type of lung cancer has its own unique stages of progression. The stages of lung cancer are determined by the size and location of the tumor, as well as whether or not it has spread to other parts of the body.
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Stages:
Stage 1: At this stage, the tumor is small and contained within the lung. It has not spread to nearby lymph nodes or other parts of the body.
Stage 2: The tumor has grown larger and may have spread to nearby lymph nodes, but has not spread to other parts of the body.
Stage 3: The tumor has grown even larger and may have spread to nearby organs, tissues, and lymph nodes.
Stage 4: At this stage, the cancer has spread to other parts of the body, such as the liver, bones, or brain.
Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC) Stages:
Limited Stage: The cancer is confined to one lung and may have spread to nearby lymph nodes.
Extensive Stage: The cancer has spread to other parts of the body, such as the liver, bones, or brain.
It is important to note that early detection of lung cancer can greatly increase the chances of successful treatment and recovery. If you are experiencing any symptoms of lung cancer or are at high risk for the disease, it is important to speak with your doctor and undergo regular screenings. Your doctor can help determine the best course of treatment based on the stage and type of lung cancer you have.
Causes of Lung Cancer

The primary cause of lung cancer is smoking. In fact, smoking is responsible for nearly 90% of all lung cancer cases. Other risk factors include:
-
Exposure to secondhand smoke
-
Exposure to radon gas
-
Exposure to asbestos and other carcinogens
-
Family history of lung cancer
-
Previous radiation therapy to the chest
Symptoms of Lung Cancer
The symptoms of lung cancer can vary depending on the stage of the cancer. In the early stages, there may be no symptoms at all. As the cancer progresses, symptoms may include:
-
Persistent cough
-
Shortness of breath
-
Chest pain
-
Hoarseness
-
Unexplained weight loss
-
Fatigue
-
Coughing up blood
-
Difficulty swallowing
Treatment of Lung Cancer
The treatment of lung cancer depends on the stage and type of cancer. Surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy are the most common treatments. In some cases, targeted therapy or immunotherapy may also be used. Treatment may also be combined with palliative care to manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
Prevention of Lung Cancer
The best way to prevent lung cancer is to not smoke or use tobacco products. If you do smoke, quitting can greatly reduce your risk of developing lung cancer. Other ways to reduce your risk of lung cancer include:
-
Avoiding secondhand smoke
-
Testing your home for radon
-
Limiting exposure to carcinogens, such as asbestos
-
Eating a healthy diet rich in fruits and vegetables
-
Exercising regularly
In conclusion, lung cancer is a serious and often deadly disease. However, by understanding the causes, symptoms, treatment, and prevention of lung cancer, you can take steps to protect yourself and seek medical attention if necessary. Remember to avoid smoking and exposure to carcinogens, and to seek medical care if you experience any symptoms of lung cancer. Early detection and treatment can greatly improve the chances of successful treatment and recovery.












