What is Diverticulitis?
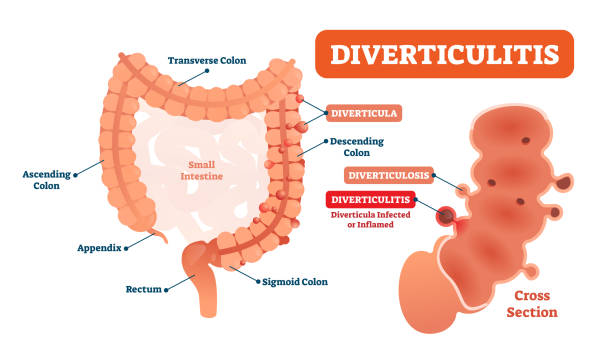
Diverticulitis is a condition in which small pouches in the digestive tract, called diverticula, become inflamed or infected. Diverticulitis affects approximately 10 percent of the population over age 40 in the United States, and is more common in the elderly. The condition can range from mild, with only a few days of abdominal pain and discomfort, to severe, requiring hospitalization and surgery.
Symptoms of Diverticulitis
The most common symptom of diverticulitis is abdominal pain. The pain usually begins in the lower left side of the abdomen and can range from mild to severe. Other symptoms may include:
• Nausea
• Fever
• Chills
• Bloating
• Constipation
• Diarrhea
• Blood in the stool
Causes of Diverticulitis
The exact cause of diverticulitis is not known. It is believed to be caused by a combination of factors, such as a low-fiber diet, obesity, and a sedentary lifestyle. A diet low in fiber can cause waste to become trapped in the diverticula, leading to infection and inflammation.
Risk Factors for Diverticulitis
• Age: The risk of diverticulitis increases with age.• Genetics: Genetics may play a role in the development of diverticulitis.
• Diet: A diet low in fiber and high in processed foods can increase the risk of diverticulitis.
• Obesity: Being overweight or obese increases the risk of diverticulitis.
• Smoking: Smoking increases the risk of diverticulitis.
Diagnosis of Diverticulitis
The diagnosis of diverticulitis is usually made based on the patient’s symptoms, physical examination, and medical history. If the diagnosis is not clear, additional tests may be done, such as a CT scan, X-ray, or blood test.
Treatment of Diverticulitis
The treatment of diverticulitis depends on the severity of the condition. Mild cases may only require a change in diet and rest. Severe cases may require antibiotics and/or surgery.
• Diet: Eating a high-fiber diet can help reduce the symptoms of diverticulitis.
• Antibiotics: Antibiotics may be prescribed to treat the infection and reduce inflammation.
• Surgery: If the infection does not respond to antibiotics, surgery may be necessary to remove the infected or inflamed tissue.
Prevention of Diverticulitis
• Eat a high-fiber diet: Eating a diet high in fiber can help reduce the risk of developing diverticulitis.
• Exercise: Regular exercise can help reduce the risk of diverticulitis.
• Maintain a healthy weight: Being overweight or obese increases the risk of diverticulitis.
• Quit smoking: Quitting smoking can reduce the risk of diverticulitis.
Conclusion
Diverticulitis is a common condition that affects the digestive tract. The exact cause of diverticulitis is not known, but it is believed to be caused by a combination of factors, such as a low-fiber diet, obesity, and a sedentary lifestyle. The treatment of diverticulitis depends on the severity of the condition, but may include antibiotics and/or surgery. The best way to prevent diverticulitis is to eat a high-fiber diet, exercise regularly, maintain a healthy weight, and quit smoking.












