Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a serious condition that affects the gums, teeth, and bones of the mouth. It is caused by the accumulation of bacteria and plaque on the teeth, which can lead to inflammation and infection of the gums. If left untreated, gum disease can result in tooth loss and other serious health problems.
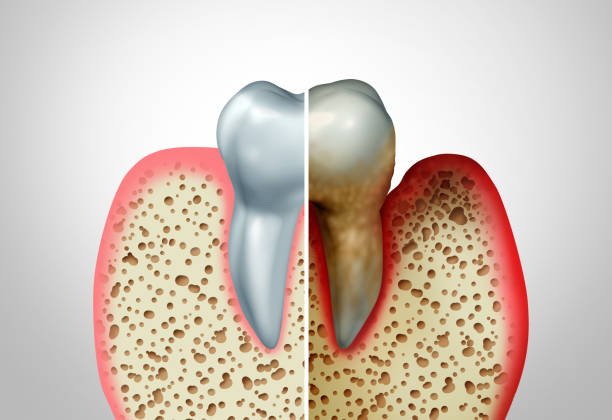
Symptoms of Gum Disease
The symptoms of gum disease can vary depending on the severity of the condition. Some common signs and symptoms of gum disease include:
- Red, swollen, or tender gums
- Bleeding gums, especially when brushing or flossing
- Receding gums, which make the teeth appear longer
- Loose or shifting teeth
- Bad breath or a persistent bad taste in the mouth
- Changes in the way the teeth fit together when biting or chewing
Types of Gum Disease
There are two main types of gum disease:
1.Gingivitis
2. Periodontitis.
Gingivitis is the milder form of gum disease and is characterized by inflammation and swelling of the gums. It is often caused by poor oral hygiene, which can lead to the buildup of plaque and bacteria on the teeth. Gingivitis can usually be reversed with proper brushing and flossing, as well as regular dental cleanings.
Periodontitis is a more serious form of gum disease that can cause permanent damage to the teeth and gums. It occurs when gingivitis is left untreated and the infection spreads to the bones and tissues that support the teeth. Periodontitis can lead to tooth loss, as well as other health problems such as heart disease and diabetes.
Causes of Gum Disease
Gum disease is primarily caused by the buildup of plaque and bacteria on the teeth. Plaque is a sticky film that forms on the teeth and contains harmful bacteria that can cause inflammation and infection of the gums. Plaque can be removed with regular brushing and flossing, but if it is not removed, it can harden into tartar, which can only be removed by a dental professional.
Other factors that can increase the risk of gum disease include:
- Smoking or using tobacco products
- Diabetes
- Poor nutrition
- Genetics
- Certain medications
- Hormonal changes, such as those during pregnancy or menopause
Preventing Gum Disease
The best way to prevent gum disease is to practice good oral hygiene. This includes brushing your teeth twice a day, flossing daily, and using an antibacterial mouthwash. You should also schedule regular dental cleanings and checkups to remove any plaque or tartar buildup and to catch any signs of gum disease early.
Other ways to prevent gum disease include:
- Eating a healthy diet that is rich in fruits and vegetables
- Quitting smoking or using tobacco products
- Managing chronic health conditions, such as diabetes
Treating Gum Disease
The treatment for gum disease depends on the severity of the condition. For mild cases of gingivitis, treatment may involve a professional dental cleaning and improved oral hygiene at home.
For more severe cases of gum disease, treatment may involve:
- Scaling and root planing, a deep cleaning procedure that removes plaque and tartar from the teeth and roots
- Antibiotics to help control the infection
- Surgery to remove infected tissue or to restore lost bone or gum tissue
If left untreated, gum disease can cause permanent damage to the teeth and gums, and can even lead to other serious health problems. If you are experiencing any signs or symptoms of gum disease, it is important to schedule an appointment with your dentist as soon as possible. With proper treatment and good oral hygiene, gum disease can be managed and even prevented altogether.











