Myopia, also known as nearsightedness, is a common vision condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a refractive error that causes distant objects to appear blurry, while close-up objects remain clear.
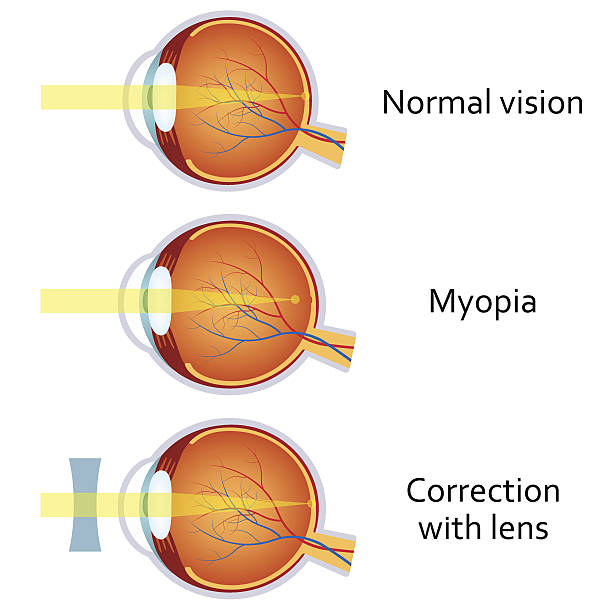
Causes of Myopia
The exact cause of myopia is not fully understood, but there are some factors that can increase the risk of developing this condition. These include:
-
Genetics: Myopia tends to run in families, and children of nearsighted parents are more likely to develop myopia.
-
Environmental factors: Certain environmental factors, such as reading or working at a computer for long periods, can increase the risk of myopia.
-
Age: Myopia is more common in children and adolescents, as the eyes are still developing.
Symptoms of Myopia
The most common symptom of myopia is blurry vision when looking at distant objects. Other symptoms may include:
-
Squinting to see distant objects
-
Headaches or eye strain
-
Difficulty driving or seeing road signs
-
Sitting close to the TV or holding objects close to the face
Diagnosis of Myopia
If you are experiencing any symptoms of myopia, it is important to see an eye doctor for an eye exam. During the exam, the doctor will check your vision and may also perform additional tests, such as a refraction test, to determine the extent of your myopia.
Treatment of Myopia
There are several treatment options available for myopia, including:
-
Eyeglasses or contact lenses: Eyeglasses or contact lenses can help correct the refractive error and improve vision.
-
Refractive surgery: LASIK or other refractive surgeries can reshape the cornea to correct the refractive error.
-
Orthokeratology: This treatment involves wearing special contact lenses at night to reshape the cornea and temporarily correct myopia.
-
Low-dose atropine eye drops: Recent studies have shown that low-dose atropine eye drops may help slow the progression of myopia in children.
In addition to these treatments, there are also some lifestyle changes that may help manage myopia, such as taking breaks when reading or using a computer, and spending more time outdoors.
Tips for Managing and Preventing Near-Sightedness
Myopia, or near-sightedness, is a common vision condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the eyeball is too long or the cornea is too curved, causing light to focus in front of the retina instead of on it, resulting in blurry vision for distant objects. While some risk factors for myopia, such as genetics, cannot be controlled, there are steps you can take to manage and prevent near-sightedness. Here are some tips:
-
Take frequent breaks from screens: Spending long periods of time looking at a computer, phone, or tablet screen can contribute to the development of myopia, especially in children. Encourage breaks every 20 minutes to give the eyes a rest.
-
Spend more time outdoors: Studies have shown that spending time outdoors, particularly in natural light, may help prevent the onset and progression of myopia. Try to spend at least 2 hours outside each day.
-
Adjust your workspace: Make sure your work area is well lit and positioned to avoid glare and eye strain. Ensure that your computer monitor is at an appropriate distance from your eyes, usually about arm's length.
-
Follow the 20-20-20 rule: Take a break every 20 minutes and look at an object 20 feet away for 20 seconds. This can help alleviate eye strain and reduce the risk of myopia.
-
Consider orthokeratology: Orthokeratology, or Ortho-K, is a non-surgical treatment that uses specially designed contact lenses to gently reshape the cornea while you sleep. This can improve vision during the day and may slow down the progression of myopia.
-
Have regular eye exams: It is important to have regular eye exams with an optometrist or ophthalmologist to detect any vision changes, including myopia, as early as possible. Early detection and treatment can help prevent further progression of myopia.
In conclusion, managing and preventing myopia involves a combination of lifestyle changes and professional intervention. By following these tips, you can help protect your eyesight and maintain clear vision. Remember to consult with your eye doctor for individualized advice on managing and preventing near-sightedness.












