HIV, or Human Immunodeficiency Virus, is a virus that attacks the immune system, causing it to weaken over time. If left untreated, HIV can lead to Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS), which is a life-threatening condition. In this blog post, we will explore the causes, symptoms, prevention, and treatment options for HIV.
Causes of HIV
HIV is caused by a virus that is transmitted through blood, semen, vaginal fluids, and breast milk. The most common ways of getting HIV include:
-
Unprotected sexual intercourse with an infected person
-
Sharing needles or syringes with an infected person
-
Mother-to-child transmission during pregnancy, birth, or breastfeeding
Symptoms of HIV
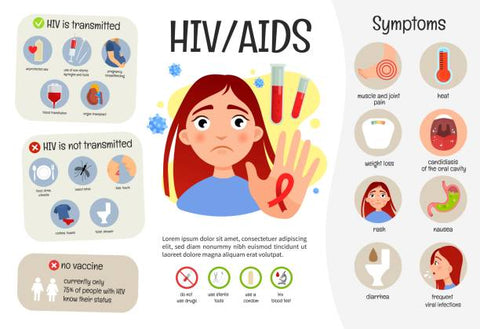
The symptoms of HIV can vary depending on the stage of the infection. During the early stage of HIV, some people may experience flu-like symptoms, such as fever, headache, and body aches. As the virus progresses, it can cause more severe symptoms, including:
-
Persistent diarrhea
-
Rapid weight loss
-
Chronic fatigue
-
Swollen lymph nodes
-
Night sweats
-
Recurrent infections
Preventions of HIV
There is currently no cure for HIV, but with proper medical care and treatment, people living with HIV can manage the virus and live long and healthy lives. Here are some tips to manage HIV:
-
Get tested: It is important to know your HIV status, as early detection and treatment can help prevent the progression of the virus and reduce the risk of transmission to others.
-
Take medication: Antiretroviral therapy (ART) is the primary treatment for HIV. These medications work by reducing the amount of HIV in the body, which can help restore the immune system and prevent the development of opportunistic infections.
-
Adhere to your medication regimen: It is important to take your HIV medication as prescribed by your healthcare provider, as missing doses can lead to drug resistance and treatment failure.
-
Practice safe sex: HIV can be transmitted through sexual contact, so it is important to use condoms or other barrier methods to prevent the transmission of the virus.
-
Avoid sharing needles: HIV can be transmitted through sharing needles or other injection equipment, so it is important to use sterile equipment or seek assistance from a healthcare provider for safe injection practices.
-
Manage other health conditions: People living with HIV may be more susceptible to other health conditions, such as high blood pressure or diabetes. It is important to manage these conditions through a healthy lifestyle and regular medical care.
-
Seek emotional support: Living with HIV can be emotionally challenging, and seeking support from friends, family, or a healthcare provider can help manage the psychological impact of the virus.
While there is no cure for HIV, these tips can help people living with HIV manage the virus and live healthy and fulfilling lives. It is important to work closely with a healthcare provider to develop an individualized treatment plan and receive regular medical care to ensure the best possible outcome.
Treatments of HIV
While there is no cure for HIV, there are several medications available that can help control the virus and prevent the progression to AIDS. These medications, called antiretroviral therapy (ART), work by reducing the amount of HIV in the body, which can help restore the immune system and prevent the development of opportunistic infections. It is important to start ART as soon as possible after diagnosis to ensure the best possible outcome.
In conclusion, HIV is a serious virus that can lead to life-threatening complications if left untreated. By understanding the causes, symptoms, prevention, and treatment options for HIV, you can take steps to protect yourself and others from this virus. Remember to always practice safe sex, get tested regularly, and seek medical care if you suspect you may have been exposed to HIV.












