What is Arthritis?
Arthritis refers to inflammation of one or more joints, resulting in pain, stiffness, and swelling. It is a broad term that encompasses a range of conditions affecting the joints and surrounding tissues. The two most prevalent types of arthritis are osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
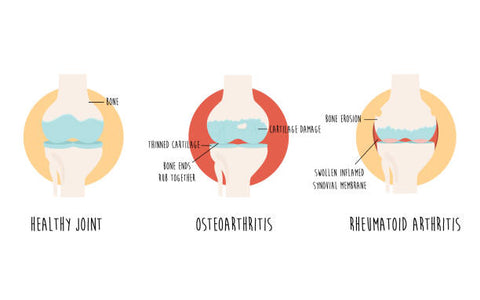
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is the most common form of arthritis and typically occurs due to wear and tear on the joints over time. It mainly affects older adults, causing the cartilage that cushions the joints to gradually break down, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility.
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis, on the other hand, is an autoimmune disease that primarily targets the joints. It occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks the synovium, the lining of the joints, resulting in inflammation and joint damage. Rheumatoid arthritis can affect individuals of any age and often leads to chronic pain, joint deformity, and functional impairment.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact causes of arthritis are still being studied, but certain factors can increase the risk of developing the condition:
- Age: The risk of arthritis, particularly osteoarthritis, increases with age.
- Gender: Rheumatoid arthritis is more common in women, while gout affects men more frequently.
- Family History: Genetics play a role in arthritis, with a family history of the condition increasing the likelihood of developing it.
- Obesity: Excess weight puts additional stress on the joints, increasing the risk of arthritis, especially in the knees, hips, and spine.
- Injuries and Joint Overuse: Previous joint injuries or repetitive stress on joints from certain occupations or sports activities can contribute to the development of arthritis.
Symptoms of Arthritis
Arthritis can manifest with various symptoms, depending on the type and severity of the condition. Common symptoms include:
-
Joint Pain: Persistent pain or aching in the affected joint(s), which may worsen with movement or after periods of inactivity.
-
Stiffness: Joint stiffness, especially in the morning or after prolonged periods of rest, making it difficult to move the joint freely."
-
Swelling: Inflammation and swelling around the joint, often accompanied by warmth and tenderness.
-
Reduced Range of Motion: Difficulty moving the joint through its full range of motion, resulting in limited flexibility.
-
Fatigue: Feeling tired and lacking energy due to the chronic pain and inflammation associated with arthritis.
- Joint Deformities: In more severe cases, arthritis can lead to joint deformities, affecting the appearance and function of the joint.
Managing Arthritis: Effective Strategies
While there is no cure for arthritis, there are several strategies that can help manage the symptoms and improve quality of life. Here are some effective approaches:
1. Medication
Depending on the type and severity of arthritis, medications may be prescribed to alleviate pain, reduce inflammation, and slow down the progression of the disease. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, and disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) are commonly used.
2. Physical Therapy
Physical therapy can be highly beneficial in arthritis management. A trained therapist can guide you through exercises and techniques that help improve joint flexibility, strengthen muscles surrounding the affected joint, and reduce pain.
3. Assistive Devices
Using assistive devices such as braces, splints, or walking aids can provide support and reduce the pressure on affected joints, making daily activities easier and less painful.
4. Lifestyle Modifications
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can have a significant impact on arthritis management. Maintain a healthy weight to reduce stress on the joints, engage in low-impact exercises like swimming or cycling, and prioritize rest and relaxation to manage pain and fatigue.
5. Heat and Cold Therapy
Applying heat or cold to the affected joints can help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation. Warm showers, heating pads, or hot packs can relax muscles and improve joint mobility, while cold packs or ice can numb the area and reduce swelling.
6. Complementary Therapies
Some individuals find relief from arthritis symptoms through complementary therapies such as acupuncture, massage therapy, or yoga. While their effectiveness may vary, it's worth exploring these options under the guidance of a qualified professional.
Conclusion
Arthritis is a prevalent condition that can significantly impact daily life. By understanding the different types of arthritis, recognizing the symptoms, and implementing effective management strategies, you can take control of your joint health and minimize the impact of arthritis on your overall well-being.
Remember, it's essential to work closely with healthcare professionals to develop a personalized treatment plan that suits your specific needs. With proper management and lifestyle adjustments, it is possible to lead a fulfilling life despite arthritis.
Author: Nikita Vishnoi BCA












