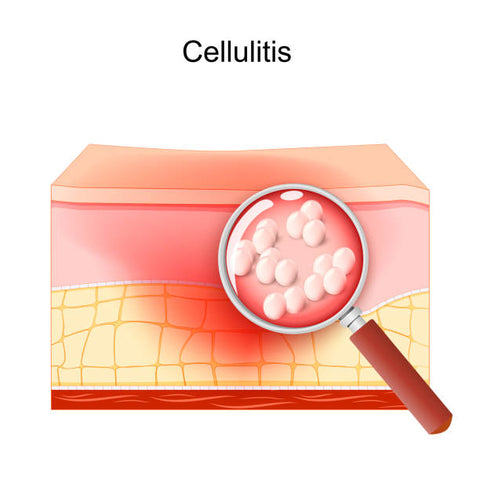
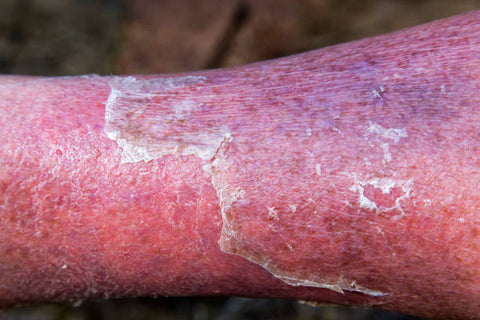
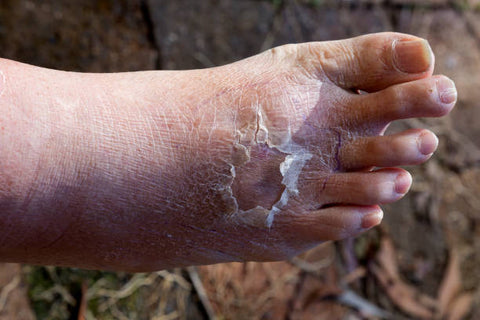
Cellulitis is a common and potentially serious bacterial skin infection that affects the deeper layers of the skin. It often starts as a small, red, swollen area and can rapidly spread, causing pain, warmth, and skin redness. Cellulitis typically occurs on the legs but can appear anywhere on the body. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent complications.
 .
. 
Causes of Cellulitis:
Cellulitis is primarily caused by bacteria, most commonly Streptococcus and Staphylococcus. The bacteria enter the skin through a crack, cut, or injury, which might be minor or unnoticed. Other factors that can lead to cellulitis include:
- Skin conditions like eczema or athlete's foot
- Surgical wounds
- Insect bites or stings
- Intravenous drug use
- Weakened immune system
- Lymphedema, which can cause fluid buildup in tissues
- Chronic swelling in the arms or legs
Symptoms of Cellulitis:
The signs and symptoms of cellulitis can vary but often include:
- Redness: The affected area becomes red and inflamed.
- Swelling: Swelling may accompany the redness.
- Pain: The skin can be tender and painful to the touch.
- Warmth: The infected area is warmer than the surrounding skin.
- Fever: In some cases, people with cellulitis may develop a fever and chills.
- Blistering: Blisters or skin abscesses might form.
Diagnosis of Cellulitis:
Diagnosing cellulitis is typically based on clinical examination. Your healthcare provider may examine the affected area and inquire about your medical history. In some cases, they may order blood tests or a culture of the wound to identify the specific bacteria causing the infection.
Treatment Options for Cellulitis:
The primary treatment for cellulitis is antibiotics. The choice of antibiotics depends on the severity of the infection and the type of bacteria involved. Other treatment options and measures include:
- Elevating the affected limb: If cellulitis occurs in the legs or arms, keeping the limb elevated can help reduce swelling.
- Pain relief: Over-the-counter pain relievers can help manage discomfort.
- Wound care: Keeping the wound clean, dry, and covered can aid the healing process.
- Rest: Resting and avoiding putting pressure on the affected area can promote recovery.
Prevention for Cellulitis:
To reduce the risk of cellulitis, consider the following preventive measures:
- Wound care: Keep cuts, scrapes, and insect bites clean and covered.
- Moisturize: If you have dry or cracked skin, use a moisturizer regularly to prevent skin from cracking.
- Good hygiene: Maintain good personal hygiene to prevent skin infections.
- Lymphedema management: If you have lymphedema, follow your healthcare provider's guidance for managing the condition.
- Prompt treatment: Seek medical attention for any skin injury that appears to be getting worse or shows signs of infection.
When to Seek Medical Help:
It's important to contact a healthcare provider if you notice any signs or symptoms of cellulitis, especially if they are worsening. Early treatment is crucial to prevent complications.
Conclusion:
Cellulitis is a common bacterial skin infection that can range from mild to severe. Prompt treatment with antibiotics and proper wound care are essential to manage the condition. Taking preventive measures and maintaining good hygiene can help reduce the risk of developing cellulitis. If you suspect you have cellulitis or notice worsening symptoms, seek medical attention to prevent potential complications.
Author: Nikita Vishnoi BCA












