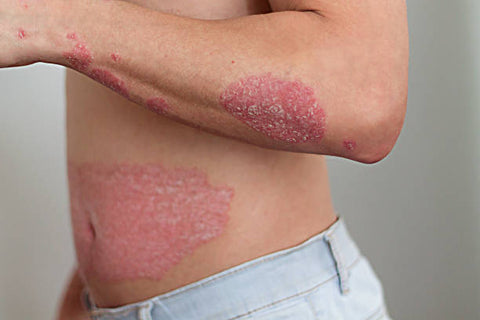
Psoriasis is a chronic skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It's characterized by the rapid growth of skin cells, leading to the formation of red, itchy, and scaly patches. While psoriasis can be managed, there is no known cure yet. Let's delve into the causes, development, treatment, and management of psoriasis.
1. Causes of Psoriasis ?
Psoriasis is an autoimmune disease, which means it occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells. While the exact cause is unknown, several factors are thought to contribute, including:
- Genetics: A family history of psoriasis increases the risk of developing the condition.
- Immune System: An overactive immune system triggers an inflammatory response, leading to the rapid skin cell turnover.
- Triggers: Certain triggers, such as stress, infections, or injuries to the skin, can exacerbate psoriasis symptoms.
2. Development of Psoriasis:
Psoriasis typically goes through several stages:
- Plaque Formation: Raised, inflamed, and scaly skin patches develop. These are often referred to as plaques.
- Progression: The plaques may grow or merge, covering larger areas.
- Remission: Symptoms can improve and even disappear for a time.
- Flare-ups: Stress, illness, or other triggers can cause symptoms to return.
3. Treatment of Psoriasis:
While there's no cure for psoriasis, several treatments can effectively manage the condition. The choice of treatment depends on the type, severity, and location of psoriasis. Common treatment options include:
- Topical Treatments: Creams, ointments, and shampoos containing corticosteroids, salicylic acid, or coal tar can alleviate mild to moderate symptoms.
- Phototherapy: Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light can slow the growth of skin cells.
- Oral or Injected Medications: For more severe cases, oral medications like methotrexate, or biologics, which target specific immune responses, may be prescribed.
4. Management of Psoriasis:
Beyond medical treatments, there are several self-care and lifestyle changes that can help manage psoriasis:
- Moisturize: Regularly apply moisturizers to keep the skin hydrated.
- Avoid Triggers: Identify and avoid factors that trigger flare-ups, such as stress or infections.
- Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle: A balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management can contribute to overall well-being.
- Skin Protection: Use sunscreen to protect your skin from UV rays.
- Stay Informed: Educate yourself about psoriasis to better understand your condition and treatment options.
Psoriasis is a complex condition that can significantly impact one's quality of life. While there's no cure, managing it effectively involves a combination of medical treatments and self-care practices. Working closely with a dermatologist or healthcare provider can help tailor a treatment plan to your specific needs, providing relief and improving your overall well-being.
Author: Nikita Vishnoi BCA












