Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder that affects both children and adults. In this blog, we will discuss the causes, symptoms, and treatment of ADHD.
Causes of ADHD
The exact causes of ADHD are unknown, but research suggests that genetics and environmental factors may play a role. Some of the possible causes of ADHD include:
-
Genetics: ADHD tends to run in families, and genes may be a contributing factor.
-
Brain Structure and Function: Studies have shown that people with ADHD have differences in the structure and function of certain areas of the brain that regulate attention and behavior.
-
Environmental Factors: Exposure to toxins or lead during pregnancy or early childhood may increase the risk of developing ADHD.
Symptoms of ADHD
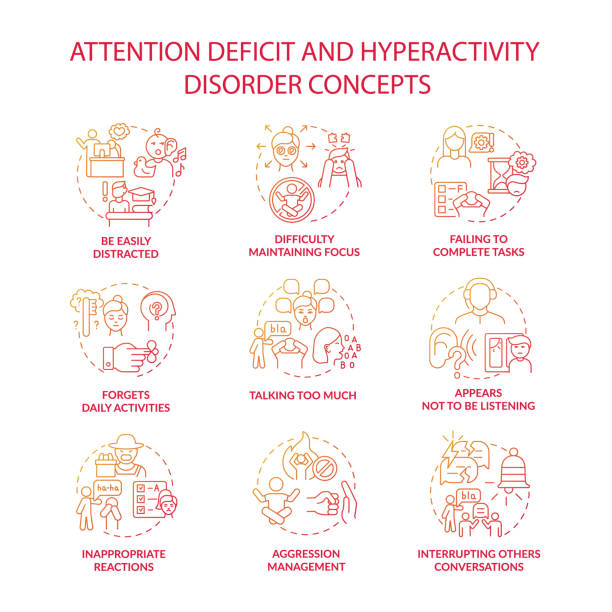
The symptoms of ADHD can vary, but they generally fall into three categories: inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. Some of the common symptoms of ADHD include:
-
Inattention: Difficulty focusing on tasks, forgetfulness, disorganization, and losing things.
-
Hyperactivity: Restlessness, fidgeting, talking excessively, and difficulty sitting still.
-
Impulsivity: Interrupting others, blurting out answers, and making impulsive decisions.
It is important to note that some of these symptoms may be common in children and adults without ADHD. However, if the symptoms are severe and persistent, they may indicate the presence of ADHD.
Treatments of ADHD
There is no cure for ADHD, but treatment can help manage the symptoms. The most effective treatment for ADHD generally involves a combination of medication, therapy, and lifestyle changes. Some of the treatment options for ADHD include:
-
Medication: Stimulants such as methylphenidate and amphetamines are often used to help manage ADHD symptoms.
-
Therapy: Behavioral therapy can help individuals with ADHD develop coping strategies and improve their social skills.
-
Lifestyle Changes: Regular exercise, healthy eating, and good sleep habits can help manage ADHD symptoms.
In addition to these treatment options, individuals with ADHD may also benefit from support groups and accommodations in school or the workplace.
Prevention of ADHD
There is no known way to prevent ADHD, but there are steps that expectant mothers can take to reduce the risk of their child developing the disorder. These include:
- Avoiding alcohol and tobacco during pregnancy
- Reducing exposure to environmental toxins
- Breastfeeding for at least six months
In conclusion, ADHD is a common neurodevelopmental disorder that affects both children and adults. The causes of ADHD are not fully understood, but genetics and environmental factors may play a role. Treatment for ADHD typically involves a combination of medication, therapy, and lifestyle changes. With the right management and support, individuals with ADHD can lead successful and fulfilling lives.












